Chapter-2 Acid And Base Class 10
Most Important Questions and Answers of Chapter 2 In Class 10 CBSE Science
Question 1.
With the help of an example explain what happens when a base reacts with a non- metallic oxide. What do you infer about the nature of non-metal oxide? (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Oxides of non-metals react with bases to form salt and water. For example, the reaction between carbon dioxide and calcium hydroxide. Calcium hydroxide, which is a base, reacts with carbon dioxide to produce salt and water.
Hence, oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature.
Question 2.
What is observed when carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water
(i) for a short duration?
(ii) for a long duration? Also write the chemical equations for the reactions involved. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(i) When CO2 is passed through lime water for short interval of time, it turns milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.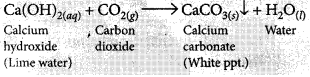
(ii) If CO2 is passed for long duration through lime water, the white precipitate formed dissolves due to the formation of soluble calcium hydrogen carbonate and the solution becomes clear.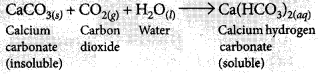
Question 3.
2 mL of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a few pieces of granulated zinc metal taken in a test tube. When the content are warmed, a gas evolves which is bubbled through a soap solution before testing. Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved and the test to detect the gas. Name the gas which will be evolved when the same metal reacts with dilute solution of a strong acid.
Answer:
It is observed that active metals like zinc react with strong bases like NaOH, KOH etc. to liberate hydrogen gas and corresponding salt.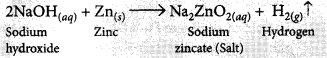
The evolution of gas is confirmed by the bubble formation in soap solution.
Test to detect H2 gas: When burning matchstick is kept on the mouth of this test tube, pop sound is heard which confirms the presence of H2 gas. When Zn metal reacts with dilute solution of strong acid, H2 gas is evolved.![]()
Question 4.
Write the names of the product formed when zinc reacts with NaOH. Also write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved. Write a test to confirm the presence of the gas evolved during this reaction. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 3.
Question 5.
To. a solution of sodium hydroxide in a test tube, two drops of phenolphthalein are added.
(i) State the colour change observed.
(ii) If dil HCl is added dropwise to the solution, what will be the colour change?
(iii) On adding few drops of NaOH solution to the above mixture the colour of the solution reappears. Why? (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(i) On adding phenolphthalein to NaOH solution, the colour becomes pink.
(ii) On adding dilute HCl solution dropwise to the same test tube, the pink colour disappears and the solution again becomes colourless.
(iii) On again adding NaOH to the above mixture, pink colour reappears because the medium becomes basic again.
Question 6.
A cloth’strip dipped in onion juice is used for testing a liquid ‘X. The liquid ‘X changes its
odour. Which type of an indicator is onion juice? The liquid ‘X turns blue litmus red. List the observations the liquid ‘X will show on reacting with the following :
(a) Zinc granules
(b) Solid sodium carbonate
Write the chemical equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
Onion juice is an olfactory indicator. Olfactory indicators give one type of odour in acidic medium and a different odour in basic medium. As the liquid ‘X’ turns blue litmus red, hence it is an acidic solution.
(a) Acids react with active metals such as zinc, magnesium etc. and evolve hydrogen gas, for example,
Zn(s) dil.H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4H2(g)
(b) Acids react with metal carbonates to give carbon dioxide with brisk effervescence.
For example, Na2CO3 + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + CO2 + H2O
Question 7.
(a) Write the chemical name and formula of marble.
(b) It has been found that marbles of Taj are getting corroded due to development of industrial areas around it. Explain this fact giving a chemical equation.
(c) (i) What happens when CO2 is passed through lime water?
(ii) What happens when CO2 is passed in excess through lime? (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(a) The chemical formula of marble (lime stone) is CaCO3. Its chemical name is calcium carbonate.
(b) Taj Mahal, one of the seven wonders of the world situated at Agra, is continuously losing its luster day by day due to rapid industrialisation which causes acid rain.
The sulphuric acid present in the acid rain causes the marble (CaCO3) to be washed off as calcium sulphate (CaSO4), leading to the deterioration of such a splendid piece of architecture.
CaCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) → CaSO4(aq) + H2Ol + CO2(g)
(c) Refer to answer 2.
Question 8.On diluting an acid, it is advised to add acid to water and not water to acid. Explain why it is so advised.
Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in laboratory.
(ii) Test the gas evolved first with dry and then with wet litmus paper. In which of the two cases, does the litmus paper show change in colour?
(iii) State the reason of exhibiting acidic character by dry HCl gas/HCl solution.
Answer:
Diluting a concentrated acid with water is a highly exothermic process. So, when water is added to concentrated acid, large amounts of heat is liberated which changes some water to steam explosively which can splash the acid and even the glass apparatus may break due to excessive heating.
Question 9.
(i) Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in laboratory.
(ii) Test the gas evolved first with dry and then with wet litmus paper. In which of the two cases, does the litmus paper show change in colour?
(iii) State the reason of exhibiting acidic character by dry HCl gas/HCl solution. (2020)
Answer:
(ii) There is no change in the colour of ‘dry’ blue litmus paper but ‘moist’ blue litmus paper turns red if brought near the mouth of the test tube.
This shows that HCl gas does not show acidic behaviour in absence of water but it shows acidic behaviour in presence of water.
(iii) When HC1 gas dissolves in water, forms hydrochloric acid solution i.e., HCl(aq) which then produces H+(aq) or H3O+(aq) ions.
HCl + H2O → H3O+ + Cl–
Due to the presence of H+ or H3O+ it shows acidic behaviour.
Question 10.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations :
(i) NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) →
(ii) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) →
(iii) HCl(aq) + H2O(l) →
Answer:
(i) 2NaOH(aq) + Zn(s) → Na2ZnO2(aq) + H2(g)
(ii) CaCO3(s) + CO2(g) + H2Ol → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
(iii) HCl(aq) + H2Ol > H3O+ Cl–(aq)
(vi) Magnesium hydroxide (Board Term 1, 2017)
Answer:
Dissociation of various substances to produce ions in their solutions are :
(i) Hydrochloric acid (HCl):
HCl(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + Cl–(aq)
(ii) Nitric acid (HNO3
HNO3(aq) ⇌ + H+aq + NO–3(aq)
(iii) Sulphuric acid (H2SO4):
H2SO4(aq) ⇌ 2H+(aq) + SO2-4(aq)
(iv) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
NaOH(aq) ⇌ Na+(aq) + OH–(aq)
(v) Potassium hydroxide (KOH) :
KOH(aq)⇌ K+(aq) + OH–(aq)
(vi) Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)2]
Mg(OH)2(aq) ⇌ Mg2++(aq) + 2OH– (aq)
Question 12.
Sugandha prepares HCl gas in her school laboratory using certain chemicals. She puts both dry and wet blue litmus papers in contact with the gas.
Name the reagents used by Sugandha to prepare HCl gas.
Answer:
Dense white fumes of hydrogen chloride gas are evolved on heating solid sodium chloride with concentrated sulphuric acid.




Comments
Post a Comment